UNDERSTANDING PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
Modern industrial automation systems are smarter and more advanced than ever before. But have you ever wondered how did they get this way? What gives them the power and capability? What drives them? The answer is the PLC.
So now the questions are ‘What does PLC stand for?’;‘What does a PLC do?’ Read on for a detailed introduction to PLCs.
What is a PLC?
First let’s learn the PLC full form. PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller. According to Wikipedia, “A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis.”
The PLC or Programmable Logic Controller is the heart and brain of industrial automation.It is a specialised computer control unit that continuously monitors the internal components and gets them to function together as a seamless, coordinated unit.
The PLC control system automatically controls the different processes, devices and components in an industrial system, and makes decisions based on a custom programme.
PLCs come in different sizes and shapes. Some can fit easily in your palm or pocket, some others need to be mounted on heavy-duty racks. They are used in a variety of applications and industries as they are fast, easy to operate and generally easy to programme.
What's inside a PLC?
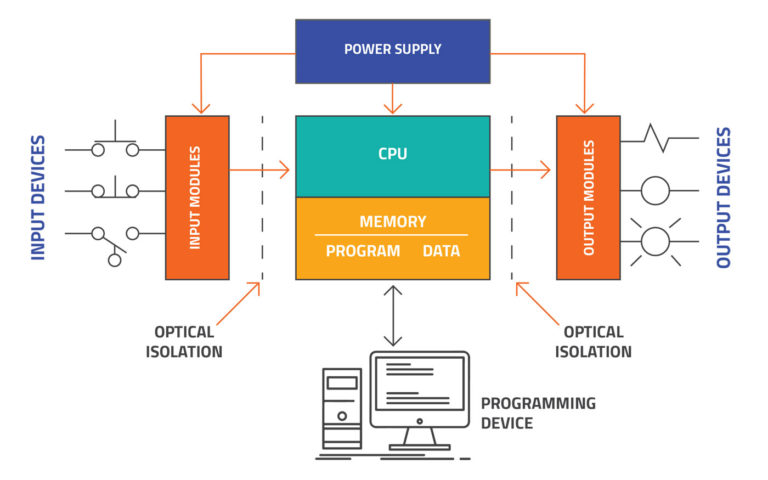
The PLC design contains some basic hardware, with each adding its own function to the PLC. The components of PLC system are:
- CPU (central processing unit or microprocessor)This is the part that runs the PLC – the brain of the microprocessor. This is where the PLC processes all the input and output signals, and saves information. The PLC has 3 types of memory:
- RAM (random access memory): this is temporary memory in use while the program is running. This memory is volatile which means it will be erased every time the power is switched off.
- ROM (read only memory): the operating system of the PLC is stored here as this is the permanent memory of the CPU. The operating system enables the PLC to execute your PLC program.
- EEPROM (electronically erasable programmable read only memory): this is a permanent memory just like the ROM, but it can be erased electronically and reused. The PLC program is stored here. EEPROM does not require a power source to maintain the memory contents, and will retain the contents of memory indefinitely.
- Input/Output (I/O) section
PLC Input and Output (I/O) section functions as the sensing organs. All field devices are connected to this section. PLC input devices receive incoming signals from external sensors such as pressure or proximity switches, converts them to low-voltage digital hints before sending them to the processor.
The output section receives the low-voltage digital signals from the processing unit and converts them into high-power hints. These high-voltage signals from the output section drive the industrial functions such as lighting, rotation, heating, movement, etc.
- Power SupplyA power supply provides the essential power to the PLC. Different PLCs use different kinds of power supplies, ranging from 24V DC to 120V AC.
- Programming sectionThis section enables inputs into the PLC controller via a keyboard. It is used to program and troubleshoot the PLC. Many a time, you will use a Windows-based computer to run the software from the manufacturer. However, programming devices can come in varying sizes, functions and capabilities.
How does a PLC work?
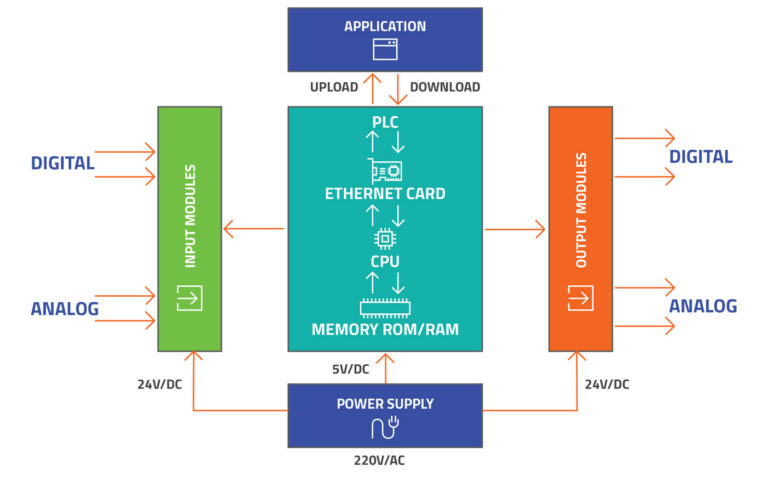
All PLCs operate as per the following steps:
- Input Scan – CPU detects the status of all input devices that are connected to the PLC (e.g.mechanical switches, proximity switches, sensors, transducers, encoders, etc.)
- Programme Scan – executes the user created program logic
- Output Scan – energises or de-energises all connected output devices connected to the PLC (e.g. relays, lights, motor starters, etc.)
- Housekeeping – this includes communications with programming terminals, internal diagnostics, etc.
Which software is used for PLC programming?
There are different types of plc programming languages but the most common programming language for PLCs is Ladder Logic. A PLC program is usually written on a computer and then downloaded to the PLC control unit.
Ladder Logic mimics control circuit schematics with ‘rungs’ of logic read left to right. Each rung represents a specific action controlled by the PLC, starting with an input or series of inputs that result in an output (coil).
Logic programming software can be easier to implement than many other programming languages because of its visual nature. The intuitive interface of ladder logic made the transition from relay logic to PLC device much simpler for many in the industry.
‘C’ programming is a more recent innovation; some PLC manufacturers provide control programming software.
Types of PLCs
In terms of physical hardware, there are two types of PLC: Compact/Fixed PLC and Modular PLC.
In compact PLCs, the power supply, CPU and communication card are contained within a single case. Compact PLCs have a fixed numberof Input/Output modules.
Modular PLCs, as the name suggests, consist of various modules and easily expanded Input and Output modules which are fitted in the rack. That’s why,this type it is also known as‘rack mounted PLC’.
PLC Applications
- Process automation
- Automatic operation and control of the air compressor system
- Bottle and liquid filling industry
- Automatic temperature control
- Belt conveyor system
- Energy monitoring system
- Production line control
- Raw material handling
Industry types
- Automotive
- Pharmaceutical
- Petrochemical
- Oil and Gas
- Steel
- Power Plant
- Food Manufacturing
- Cement Industry
- Paper Industry
- Glass Manufacturing
- Raw Material Handling Industry
Messung: Pioneer of India’s first indigenous PLC
As industrial automation & control systems continue to advance, growing in function and sophistication, PLCs too will have to evolve to keep pace. To build a future-ready system with best-in-class PLCs and automation system components, contactMessung, pioneer and leading PLC manufacturer in India.
Messung was founded in 1981 when the founder began developing a prototype PLC in a humble garage. By 1984, India’s firstindigenous 1-bit processor-based PLC was launched – and went on to transform industry, replacing the traditional relay contactor logic.
Since then, it’s been one continuous journey of innovation and excellence in industrial automation.
Messung’s programmable controllers, Remote I/Os, HMIs and SCADA solutions have enabled industries, OEMs and automation system integrators achieve top-of-the-line performance and efficiencies. Messung’s rugged, IoT-enabled industrial controllers are gamechangers with their inbuilt I/O, integrated HMI panels and advanced features while Messung’s Process Automation, Servo & Motion Control Automation, and General Purpose Automation solutions have proven themselves across the gamut of industries with their flexibility, efficiency and long service life.
Messung Industrial Automation & Control division also offers PLC panels for remote control, SCADA applications, VFD drives and servo drives.
